Common Heart Tests for Newborns: Essential Guide
As a pediatric cardiologist practicing in Vijayawada, I understand the anxiety that new parents feel when discussing their baby’s heart health. The first few days after birth are crucial for detecting potential heart problems, and common heart tests for newborns serve as vital tools in ensuring your baby’s cardiovascular wellbeing. These screening procedures can identify serious conditions early, often before symptoms become apparent.
Heart defects affect approximately 8 out of every 1,000 babies born in India, making early detection through comprehensive screening essential. While this statistic might seem concerning, the good news is that modern diagnostic techniques allow us to identify and treat most heart conditions successfully when caught early.
Understanding the Importance of Newborn Heart Screening
Congenital heart defects represent the most common type of birth defect globally. Many of these conditions, particularly critical congenital heart defects (CCHDs), can be life-threatening if not detected promptly. However, some heart abnormalities may not produce obvious symptoms in the first few days of life.
The primary goal of implementing common heart tests for newborns is to identify babies who need immediate medical intervention. Early detection significantly improves treatment outcomes and can prevent serious complications that might arise if these conditions go undiagnosed.
In my practice, I’ve seen how timely screening has made the difference between life and death for numerous infants. Therefore, understanding these tests empowers parents to make informed decisions about their baby’s healthcare journey.
Primary Screening: Pulse Oximetry Test
What Is Pulse Oximetry?
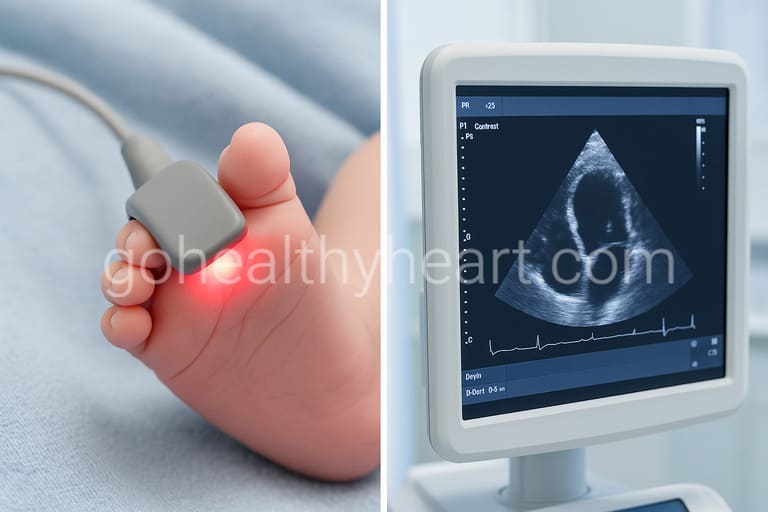
Pulse oximetry stands as the cornerstone of newborn heart screening programs worldwide. This simple test measures the oxygen saturation level in your baby’s blood using a small sensor placed on the skin. The device works by shining light through the skin to detect how much oxygen the red blood cells are carrying.
When and How It’s Performed
The pulse oximetry screening typically occurs between 24 to 48 hours after birth, before your baby leaves the hospital. The healthcare team places small sensors on your baby’s right hand and one foot simultaneously. These sensors are connected to a monitor that displays the oxygen saturation readings.
The test takes only a few minutes and causes no discomfort to your baby. Normal oxygen saturation levels should be 95% or higher. If the readings fall below this threshold, further evaluation becomes necessary to rule out critical heart defects.
Why This Test Matters
Low oxygen levels in the blood often indicate that the heart isn’t pumping effectively or that there’s an abnormal connection between blood vessels. Pulse oximetry can detect approximately 75% of critical congenital heart defects, making it an invaluable screening tool.
Comprehensive Evaluation: Echocardiogram
Understanding Echocardiography
When common heart tests for newborns indicate potential problems, an echocardiogram becomes the next crucial step. This ultrasound examination creates detailed moving images of your baby’s heart, showing the heart chambers, valves, and blood flow patterns in real-time.
The Procedure Experience
During an echocardiogram, your baby lies comfortably while a trained technician applies warm gel to the chest area. A small ultrasound probe is then gently moved across the chest to capture images from different angles. The entire process typically takes 30 to 60 minutes.
Parents can remain with their babies throughout the examination to provide comfort. The test is completely painless and involves no radiation exposure, making it safe for repeated use if necessary.
Diagnostic Capabilities
Echocardiograms can detect virtually all types of congenital heart defects, including:
- Septal defects (holes in the heart walls)
- Valve abnormalities
- Problems with major blood vessels
- Heart rhythm irregularities
- Poor heart muscle function
This comprehensive imaging allows pediatric cardiologists to assess not only the heart’s structure but also how well it functions.
Additional Diagnostic Tools
Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG)
An electrocardiogram records the electrical activity of your baby’s heart through small electrodes placed on the chest, arms, and legs. This test helps evaluate heart rhythm patterns and can detect electrical conduction problems that might not be visible on an echocardiogram.
The ECG is particularly useful for identifying arrhythmias (irregular heartbeats) that can occur in newborns. Like other common heart tests for newborns, this procedure is quick, painless, and provides valuable information about heart function.
Chest X-ray Imaging
Chest X-rays offer another perspective on heart health by showing the size and shape of the heart within the chest cavity. These images can reveal if the heart is enlarged or if there’s fluid accumulation in the lungs, which might indicate heart failure.
While chest X-rays involve minimal radiation exposure, they’re only used when medically necessary and provide important diagnostic information that complements other testing methods.
Advanced Imaging Techniques
In complex cases, additional imaging studies such as cardiac MRI or CT scans might be recommended. These advanced techniques provide extremely detailed three-dimensional images of heart structures and are particularly useful for surgical planning.
Prenatal Heart Screening: Fetal Echocardiography
Early Detection During Pregnancy
Fetal echocardiography represents an important category of heart screening that occurs before birth. This specialized ultrasound examination of the baby’s heart is typically performed between 18 to 24 weeks of pregnancy when certain risk factors are present.
Risk Factors Requiring Fetal Heart Screening
Several circumstances warrant fetal echocardiography:
- Family history of congenital heart disease
- Maternal diabetes or other medical conditions
- Abnormal findings on routine pregnancy ultrasounds
- Previous child with heart defects
- Maternal age over 35 years
Early detection through fetal screening allows healthcare teams to prepare for delivery and immediate postnatal care, significantly improving outcomes for babies with heart defects.
When Are Heart Tests Recommended?
Clinical Indicators
Healthcare providers recommend common heart tests for newborns when specific signs or symptoms are present:
Physical Signs:
- Cyanosis (bluish coloring of lips, fingers, or toes)
- Rapid or difficult breathing
- Poor feeding or excessive fatigue during feeding
- Unusual heart sounds (murmurs)
Risk Factors:
- Premature birth
- Low birth weight
- Family history of heart defects
- Maternal health conditions during pregnancy
Screening Protocols
Most hospitals now implement routine pulse oximetry screening for all newborns as part of standard care. However, additional testing depends on individual risk factors and clinical findings during the physical examination.
Understanding Test Results and Next Steps
Normal Results
When common heart tests for newborns show normal findings, parents can feel reassured about their baby’s heart health. However, it’s important to remember that some minor heart defects might not be detectable immediately after birth and could be identified during routine pediatric check-ups.
Abnormal Findings
If screening tests suggest a heart problem, the next step involves referral to a pediatric cardiologist for comprehensive evaluation. This doesn’t necessarily mean your baby has a serious condition, as some abnormal findings resolve on their own as the baby grows.
Treatment Options
Treatment approaches vary depending on the specific type and severity of heart defect:
Conservative Management:
- Regular monitoring and follow-up
- Medications to support heart function
- Nutritional support for proper growth
Interventional Procedures:
- Cardiac catheterization for certain defects
- Minimally invasive surgical repairs
- Open-heart surgery when necessary
When Surgery Becomes Urgent: Critical Cases Requiring Immediate Intervention
While many heart conditions detected through common heart tests for newborns can be managed with medication or monitoring, some situations demand immediate surgical intervention. Understanding these critical scenarios helps parents recognize the urgency and importance of prompt medical care.
Identifying Critical Situations
Doctors determine the need for emergency surgery in newborns based on several life-threatening indicators. These critical assessments often follow abnormal results from initial screening tests and comprehensive echocardiographic evaluation.
Severe Clinical Presentations:
Critical congenital heart defects (CCHDs) may manifest as severe cyanosis, where the baby’s skin, lips, and fingernails appear distinctly blue despite oxygen support. This persistent blue coloring indicates that the heart cannot adequately oxygenate the blood, requiring immediate intervention.
Poor oxygen levels that don’t improve even with supplemental oxygen therapy signal that structural heart problems are preventing proper blood circulation. Additionally, signs of heart failure in newborns include rapid breathing, swelling in the extremities, and decreased cardiac output affecting vital organs.
Echocardiogram Findings Requiring Surgery
When common heart tests for newborns reveal specific structural abnormalities through echocardiography, immediate surgical planning becomes necessary. These critical findings include:
Obstructed Blood Flow: Complete or severe blockages in major blood vessels prevent adequate circulation to vital organs. These obstructions can occur in the aorta, pulmonary arteries, or within the heart chambers themselves.
Underdeveloped Heart Chambers: Some babies are born with heart chambers that are too small to function effectively. This underdevelopment can affect either the left or right side of the heart, compromising the organ’s ability to pump blood efficiently.
Transposed Great Arteries: This condition involves the switching of the two main arteries leaving the heart, creating a life-threatening circulation pattern that requires immediate correction.
Life-Threatening Conditions Requiring Early Surgery
Certain heart defects identified through newborn screening programs typically require surgical intervention within the first days or weeks of life. Understanding these conditions helps parents prepare for the medical journey ahead.
Transposition of the Great Arteries (TGA): This condition occurs when the two main arteries carrying blood away from the heart are switched. Babies with TGA often require an arterial switch operation within the first few weeks of life to restore normal blood circulation patterns.
Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome (HLHS): In this complex condition, the left side of the heart is severely underdeveloped. HLHS typically requires a series of surgeries, with the first procedure usually performed within the first week of life to ensure adequate blood flow to the body.
The Importance of Early Detection
The critical nature of these conditions underscores why common heart tests for newborns are so essential. Early identification through pulse oximetry screening and subsequent echocardiographic evaluation allows medical teams to:
Stabilize the Baby: Immediate medical support can maintain circulation and oxygenation while preparing for surgery. This stabilization period is crucial for optimizing surgical outcomes.
Plan Surgical Intervention: Advance preparation allows surgical teams to coordinate complex procedures and ensure all necessary resources are available. This planning significantly improves surgical success rates.
Support Family Preparation: Early diagnosis gives families time to understand the condition, meet with surgical teams, and prepare emotionally for the journey ahead.
Post-Surgical Outcomes
While the prospect of newborn heart surgery can be overwhelming for parents, it’s important to understand that outcomes have improved dramatically over recent decades. Many babies who undergo these critical procedures go on to live full, active lives with appropriate follow-up care.
Modern pediatric cardiac surgery techniques, combined with advanced post-operative care, have significantly increased survival rates for even the most complex heart defects. Regular follow-up with pediatric cardiologists ensures continued monitoring and any necessary adjustments to treatment plans.
Living with Congenital Heart Disease
Long-term Outcomes
Many children born with heart defects go on to live normal, active lives with proper medical care. Advances in pediatric cardiology and cardiac surgery have dramatically improved outcomes over the past decades.
Family Support and Resources
Receiving a diagnosis of congenital heart disease can be overwhelming for families. However, numerous support resources are available, including patient advocacy groups, online communities, and specialized healthcare teams dedicated to helping families navigate this journey.
Prevention and Risk Reduction
Prenatal Care Importance
While not all heart defects can be prevented, maintaining good prenatal care significantly reduces risks. This includes:
- Regular prenatal check-ups
- Proper nutrition and vitamin supplementation
- Avoiding harmful substances during pregnancy
- Managing maternal health conditions effectively
Genetic Counseling
For families with a history of congenital heart disease, genetic counseling can provide valuable information about recurrence risks and available screening options for future pregnancies.
The Indian Healthcare Context
Availability of Screening Programs
In India, newborn heart screening programs are expanding rapidly, with many government and private hospitals implementing routine pulse oximetry screening. However, availability can vary between urban and rural areas.
Cost Considerations
Most basic screening tests are relatively affordable and increasingly covered by government health schemes and insurance plans. The cost of comprehensive evaluation and treatment has also become more accessible through various healthcare initiatives.
Choosing the Right Healthcare Provider
Pediatric Cardiology Expertise
When heart problems are suspected, seeking care from qualified pediatric cardiologists is crucial. These specialists have specific training in diagnosing and treating heart conditions in children.
Hospital Facilities
Look for healthcare facilities that offer comprehensive pediatric cardiac services, including advanced imaging capabilities, cardiac catheterization laboratories, and pediatric cardiac surgery programs when needed.
Frequently Asked Questions
The most frequently performed common heart tests for newborns in Indian hospitals include pulse oximetry screening, echocardiograms, and physical examinations by pediatricians. Pulse oximetry is increasingly becoming standard practice in major hospitals across India, while echocardiograms are performed when screening results are abnormal or when risk factors are present.
While pulse oximetry screening is not universally mandatory across all Indian states, many leading hospitals have adopted it as standard practice. The Indian Academy of Pediatrics recommends routine screening, and several state governments are implementing policies to make it mandatory in government healthcare facilities.
Pulse oximetry can detect approximately 75% of critical congenital heart defects, while echocardiograms are highly accurate, detecting nearly 100% of significant heart abnormalities. The combination of physical examination and these tests provides excellent diagnostic accuracy for identifying babies who need immediate medical attention.
If your baby fails pulse oximetry screening, don’t panic. The healthcare team will repeat the test and may perform additional evaluations including an echocardiogram. Failed screening doesn’t automatically mean your baby has a serious heart problem, as factors like breathing difficulties or circulation issues can also affect results.
Yes, common heart tests for newborns are extremely safe. Pulse oximetry and echocardiograms are non-invasive, painless procedures that pose no risk to babies. Even chest X-rays, when necessary, involve minimal radiation exposure that’s considered safe for diagnostic purposes.
Pulse oximetry results are available immediately during the test. Echocardiogram results are typically available within a few hours, though complex cases might require additional review by pediatric cardiologists. Most parents receive results before leaving the hospital or within 24-48 hours.
If a heart defect is identified, your baby will be evaluated by a pediatric cardiologist who will determine the severity and recommend appropriate treatment. Many heart defects are manageable with medication, while others might require surgical intervention. Early detection significantly improves treatment success rates.
Yes, fetal echocardiography can detect many heart defects during pregnancy, typically between 18-24 weeks. This specialized ultrasound is recommended for high-risk pregnancies and allows healthcare teams to prepare for immediate postnatal care if needed.
Basic pulse oximetry screening is usually included in standard newborn care packages. Echocardiograms typically cost between ₹2,000-5,000 in private hospitals, though costs may be lower in government facilities. Many insurance plans and government health schemes now cover these essential screening tests.
Even with normal screening results, parents should maintain regular pediatric check-ups and watch for signs like poor feeding, rapid breathing, bluish coloring, or excessive fatigue. Some heart conditions might not be apparent immediately after birth and could be detected during routine well-child visits.
Conclusion
Common heart tests for newborns represent one of the most important medical advancements in pediatric care. These screening procedures provide parents and healthcare providers with crucial information about a baby’s heart health during the most critical period after birth.
As a pediatric cardiologist, I strongly encourage all parents to ensure their newborns receive appropriate heart screening. Early detection through these simple, safe tests can literally save lives and prevent serious complications that might otherwise go unnoticed.
Remember that receiving abnormal test results doesn’t automatically indicate a serious problem. Many screening abnormalities require only monitoring, while others can be successfully treated with excellent long-term outcomes. The key is early detection and appropriate medical care.
If you’re in Vijayawada or surrounding areas and have concerns about your baby’s heart health, don’t hesitate to seek expert evaluation. Together, we can ensure your child gets the best possible start in life with comprehensive cardiac care.
For expert consultation and newborn heart screening in Vijayawada, schedule an appointment today with Dr. Anusha Kattula.



